This year’s Apple Worldwide Developer Conference (WWDC) was filled with announcements and first-looks for upcoming software releases that promise to benefit every business, no matter its size. Now with WWDC 2023 behind us, we look at what Apple has planned for the year ahead in the space of device management for macOS and iOS.
Platform SSO
During WWDC 22, Apple announced platform SSO building upon SSO extension built into macOS Catalina. My thoughts on this announcement were that it’s now in the hands of the IdPs to implement the protocols and build the necessary extensions, while device management vendors will need to update their extensible SSO to support the changes.
Okta and Microsoft heard the macadmin community with Microsoft now support platform SSO, with Okta coming soon. Apple have taken note of the IDP adoption and doubled down by adding a slew of new features for platform SSO, such as:
- Environments where an account is managed by an IDP federated with Azure will be able to authenticate to platform SSO as support for WS-Trusts federation has been added.
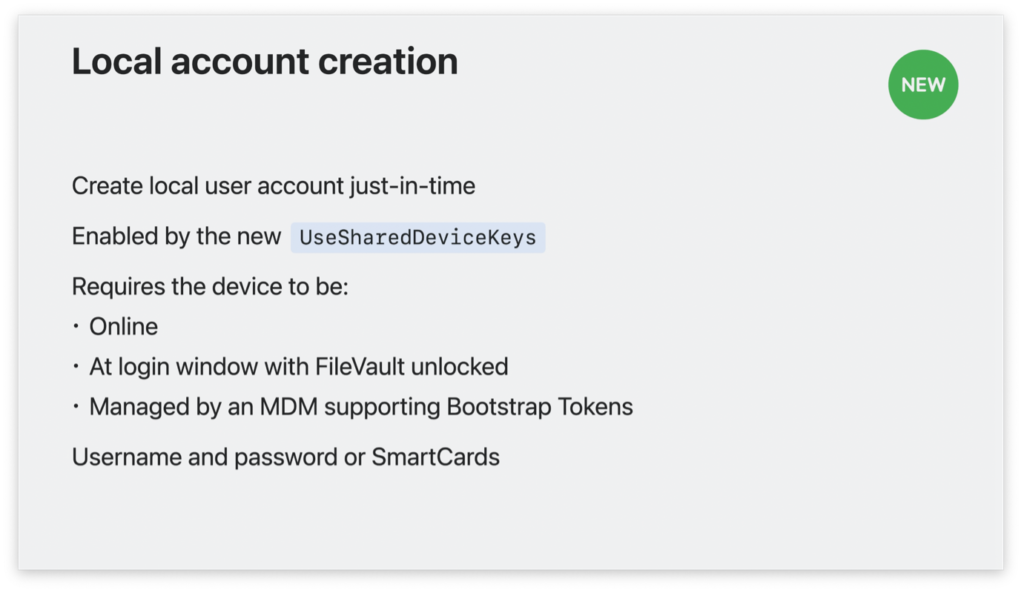
- Platform SSO can now facilitate account management in shared deployments, allowing users to use their cloud IDP or smart card to log into a fully booted Mac with Filevault unlocked and create a local admin.
- Group membership can be used to granularly manage permissions of IdP users in the operating system. Meaning, every time a user authenticates with the IdP, their group membership is updated.
- The use of non-local IdP user accounts at authorisation prompts.
- Platform SSO will now expand the use of IdP credentials to users who don’t have a local user account on the Mac for authorisation purposes.
The enhancements to platform SSO mark a significant step forward in streamlining authentication processes and enhancing user experience on macOS with the enterprise. It’s reassuring to see industry leaders like Okta and Microsoft responding to the macadmin community’s feedback by pledging support for platform SSO. Apple too, has demonstrated their commitment to IDP adoption by introducing a range of new features that bolster the capabilities of platform SSO.
Changes to Automated Device Enrolment for macOS
Automated Device Enrolment has become a crucial aspect of macOS deployment and security in organisations. Apple’s continuous efforts to enhance deployment processes and bolster security for macOS devices have resulted in ground-breaking features.
One of these being the advancement to FileVault during Automated Device Enrolment, which makes sure managed Mac computers have encrypted internal storage right from the start. This allows organisations to launch FileVault encryption during the setup assistant, with the flexibility to display the FileVault Recovery Key or securely store it as a personal recovery key. This proactive step exemplifies Apple’s commitment to data protection, empowering organisations to fortify encryption practices and safeguard sensitive information.
Apple’s Automated Device Enrolment now also empowers organisations to enforce a minimum operating system (OS) version during device enrolment. Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions can now seamlessly guide users through necessary software updates or upgrades to meet the specified minimum OS version. This development guarantees that all organisation-owned devices are aligned with the required OS version before production of deployment, streamlining the setup process and maintaining a secure device environment.
Building upon these advancements, macOS 14 also introduces an innovative feature for devices registered with Apple School Manager or Apple Business Manager. In cases where device management enrolment is missed during initial setup, a full-screen set up experience is displayed. This allows users to delay enrolment once, dismissing the screen temporarily for eight hours. Upon expiration, users are then prompted to either perform enrolment or erase their Mac.
Before the dismissal expires, a follow-up enrolment option is provided in System Settings. This enhancement ensures device enrolment into device management is achieved, even if internet connectivity is absent during the initial setup – resulting in fewer unmanaged devices and further enhancing organisational control and security.
Through these continual advancements, Apple continues to demonstrate its commitment to enhancing macOS deployment practices and fortifying security measures. By embracing these features, organisations can establish a robust and secure macOS environment, enabling efficient device management and safeguarding critical data.
More notable changes and enhancements for macOS
Passcode Config
In the realm of password security, Apple continues to prioritise the protection of sensitive data, particularly in corporate and educational environments. Acknowledging the need for more robust password requirements, Apple has introduced a remarkable level of flexibility in this area.
By allowing password policies to be defined as regular expressions, administrators gain enhanced control over password complexity. While working with regular expressions can be challenging, Apple advises utilising existing password policy options whenever feasible. Additionally, Apple has strengthened Password Compliance management for macOS 14, refining the way compliance is communicated to users. When a stricter password policy is implemented, users will receive a notification indicating that their current password may not be compliant.
This notification will only appear if the password fails to meet the installed payload policy. During the subsequent login, compliance will be assessed, and if the password remains non-compliant, the user will receive a notification with the option to change the password immediately or later. Until the password is compliant, the same notification will persistently appear with each login attempt, ensuring users are continually prompted to update their password for improved security. Through these advancements, Apple exhibits its thought leadership by emphasising the importance of password security and providing tools that empower administrators and users alike to safeguard their digital assets effectively.
New System Settings Restrictions
With each new version of macOS, organisations gain more options to restrict specific functionalities within System Settings, offering granular controls and an improved user experience.
These features include:
- The ability to disable users from modifying internet accounts or signing into Apple ID, preventing them from changing hostnames or the start-up disk.
- Restricting the setup of Time Machine, to allow organisations to limit users from adding or removing fingerprints and block the use of Siri. While administrators can be prevented from creating new users in the Users and Groups section.
Additionally, macOS allows organisations to limit end users’ management of sharing services like:
- File sharing
- Printer sharing
- ARD remote management
- Remote Apple events
- Internet sharing
- Bluetooth sharing
By providing these comprehensive restrictions, macOS empowers organisations to customise the user experience according to their specific needs and security requirements. These fine-grained controls promote a secure and efficient operating environment for macOS deployments.
Allowing more Applications to Become Managed
With macOS 14, Apple introduces powerful features that streamline application management that provide organisations with enhanced control and improved data security.
macOS 14 simplifies application management by automatically categorising any application deployed to the applications directory as ‘managed’. Organisations can utilise MDM to define the retention or removal of managed applications during unenrolment. MDM even enables complete application uninstallation, removing associated bundles while preserving installed data and scripts in other locations.
To bolster data security, macOS 14 segregates data from managed applications onto a separate volume during User Enrolment or account-driven Device Enrolment. This separation boosts the integrity and security of sensitive information, minimising the risk of data breaches and ensuring compliance.
By leveraging these streamlined application management features, organisations can optimise deployment processes, maintain a secure macOS environment, and enhance productivity and data security.
Updates for iOS and iPadOS Management
Added Return to Service
With the implementation of streamlined device management processes, the resetting and re-enrolment of devices has become fully automated and significantly quicker. When a managed device receives an erase command from the MDM solution, it can include Wi-Fi details and specify which MDM solution should enrol the device. The Wi-Fi profile is essential for device activation unless alternative internet connectivity options are available, like a tethered connection.
For devices registered in Apple School Manager or Apple Business Manager, the MDM configuration can be omitted, prompting the device to check for an enrolment profile during activation. This feature is particularly useful in scenarios where interactive authentication for Automated Device Enrolment would typically be required.
Utilising the provided information, the device erases all data and seamlessly proceeds to the Home Screen, ready for immediate use. Throughout this process, the device’s previously selected language and region settings are applied. The preservation of an existing eSIM depends on the configuration of the PreserveDataPlan key, ensuring flexibility in preserving cellular data plans when applicable.
Enforce a minimum version of iOS or iPadOS
Similar to its macOS counterpart, MDM solutions can now be empowered to enforce a minimum OS version during device enrolment. MDM solutions can now seamlessly guide users through necessary software updates or upgrades to meet the specified minimum OS version. This development guarantees that all organisation-owned devices are aligned with the required OS version before production deployment, streamlining the setup process and maintaining a secure device environment.
MDM with Private Cellular Networks
iOS 17 and iPadOS 17 bring significant advancements in network management, empowering organisations to optimise connectivity and streamline operations. Apple continues to prioritise the evolving needs of enterprise network environments with features like Private Cellular Network configuration, 5G network slicing management, eSIM preservation, and deprecations.
Organisations can now configure device settings for their private 5G and LTE networks using MDM solutions or configuration profiles with Private Cellular Network payloads. This feature allows organisations to customise specific settings, like enabling 5G Standalone (SA) or prioritising cellular over Wi-Fi connections. Geofence activation further enhances network switching capabilities, seamlessly enabling private network eSIM or physical SIM when entering defined coverage areas.
iOS 17 and iPadOS 17 introduce the ability to assign network slices to managed apps on carrier’s 5G SA networks. Organisations can route all traffic for designated apps to specific network slices identified by Data Network Names (DNNs). This granular control over network traffic allocation ensures optimized performance and efficiency for managed apps, enhancing the overall user experience.
iOS 17 and iPadOS 17 now preserve eSIMs when devices are erased due to passcode policy violations. This change provides greater flexibility and convenience, ensuring that eSIMs remain intact even in situations of passcode-related device wipes.
With the advanced network management capabilities introduced in iOS 17 and iPadOS 17, organisations can fine-tune their private cellular networks, manage 5G network slicing for optimised app performance and preserve eSIMs during passcode policy wipes. These features underscore Apple’s commitment to providing organizations with robust tools to enhance network efficiency, security, and control, enabling them to build and maintain robust network infrastructures.
Reminder for Some Deprecations
Apple has taken a proactive approach in reminding us on their plan to execute previously announced deprecations. Notably, Apple has decided to remove the APN payload and top-level cellular keys from the Device Information Query. This strategic move not only streamlines the querying process but also aligns with Apple’s vision for a more efficient and secure ecosystem.
Going forward, Apple recommends utilising the com.apple.cellular.payload and ServicesSubscriptions response as alternatives, offering enhanced functionality and improved user experience.
Looking ahead, Apple has plans to introduce further changes in a future release, specifically with regards to listed restrictions, which will require supervision. This forward-thinking approach ensures that device management remains robust and in line with organisational policies. Apple also recognises the importance of personalisation and security by implementing restrictions that will apply exclusively to the individual logged into their Apple ID on the device.
Throughout this article, we have discussed the major changes with device management from WWDC 2023, and here at Mac Centre, we highly recommend that your organisation sign up to Apple Seed for IT as betas for iOS 17 and macOS Sonoma are now available. This will allow your organisation to start testing and building test plans to ensure that you are supported with the launch of these new OS and features.